Questions numbered 1 through 25 count 2 points each (50 points).
| B |
1. |
(1) |
The role of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) in activation of the complement cascade via the classical pathway. |
| | (2) | The role of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) in activation of the complement cascade via the alternate pathway. |
| C |
2. |
(1) |
The association between a Type II hypersensitivity and the disease known as autoimmune hemolytic anemia. |
| | (2) | The association between a Type II hypersensitivity and the disease known as pemphigus. |
| A |
3. |
(1) |
The similarities between a T-cell receptor molecule and the Fab (antigen binding domain) fragment of IgG. |
| | (2) | The similarities between a T-cell receptor molecule and the Fc (receptor binding domain) fragment of IgG. |
| A |
4. |
(1) |
The immunogenicity of a typical exotoxin. |
| | (2) | The immunogenicity of a typical endotoxin. |
| B |
5. |
(1) |
The communicability of a disease to which 60% of the affected population is immune. |
| | (2) | The communicability of a disease to which 20% of the affected population is immune. |
| A |
6. |
(1) |
The ability of a B-cell to present antigen to a T-cell. |
| | (2) | The ability of a B-cell to present antigen to a macrophage. |
| A |
7. |
(1) |
The virulence of an organism with an LD50 of 5 x 103. |
| | (2) | The virulence of an organism with an LD50 of 5 x 107. |
| B |
8 |
(1) |
The propensity for intracellular pathogens to produce acute disease. |
| | (2) | The propensity for intracellular pathogens to produce chronic disease. |
| B |
9. |
(1) |
The importance of macrophage activation to the elimination of extracellular bacteria. |
| | (2) | The importance of macrophage activation to the elimination of intracellular bacteria. |
| B |
10. |
(1) |
The probability that an antigen derived from an extracellular bacterium would be presented to a T-cell via the Class I MHC molecule. |
| | (2) | The probability that an antigen derived from an extracellular bacterium would be presented to a T-cell via the Class II MHC molecule. |
| C |
11. |
(1) |
The number of Complementarity Determining Regions (CDRs) normally found in an immunoglobulin light chain. |
| | (2) | The number of Complementarity Determining Regions (CDRs) normally found in an immunoglobulin heavy chain. |
| B |
12. |
(1) |
The role of cytotoxic T-cells in the process known as antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity. |
| | (2) | The role of K-cells in the process known as antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity. |
| A |
13. |
(1) |
The probability of finding a CD8 molecule on the surface of a cytotoxic T-cell. |
| | (2) | The probability of finding a CD8 molecule on the surface of a helper T-cell. |
| A |
14. |
(1) |
The ability of IgG antibody to cross the placenta and help to protect a fetus in utero. |
| | (2) | The ability of IgM antibody to cross the placenta and help to protect a fetus in utero. |
| A |
15. |
(1) |
The importance of opsonizing antibodies in preventing disease caused by an organism such as Streptococcus pneumoniae whose sole virulence mechanism is the production of a capsule. |
| | (2) | The importance of antitoxin antibodies in preventing disease caused by an organism such as Streptococcus pneumoniae whose sole virulence mechanism is the production of a capsule. |
| B |
16. |
(1) |
The number of polypeptide chains that make up a molecule of IgG. |
| | (2) | The number of polypeptide chains that make up a molecule of IgM. |
| A |
17. |
(1) |
The amount of precipitate formed when an antigen-antibody ratio is close to 1:1. |
| | (2) | The amount of precipitate formed when an antigen-antibody ratio is close to 1:10. |
| B |
18. |
(1) |
The ability of Protein H to inhibit the activation of the complement cascade by cleaving cell membrane bound C3b. |
| | (2) | The ability of Factor I to inhibit the activation of the complement cascade by cleaving cell membrane bound C3b. |
| A |
19. |
(1) |
The number of structural domains in the alpha chain of a Class I MHC molecule. |
| | (2) | The number of structural domains in the alpha chain of a Class II MHC molecule. |
| A |
20. |
(1) |
The probability that the idiotypic network hypothesis for regulation of the humoral response occurs when antibody levels are relatively high. |
| | (2) | The probability that the idiotypic network hypothesis for regulation of the humoral response occurs when antibody levels are relatively low. |
| C |
21. |
(1) |
The ability of the complement complex C3bBbC3b to cleave the component C5. |
| | (2) | The ability of the complement complex C4b2b3b to cleave the component C5. |
| A |
22. |
(1) |
The role of the thymus in the maturation of T-cells. |
| | (2) | The role of the thyroid in the maturation of T-cells. |
| B |
23. |
(1) |
The role of the Class II MHC molecule in the recognition of antigen. |
| | (2) | The role of the Class II MHC molecule in the presentation of antigen. |
| A |
24. |
(1) |
The role of the spleen in collecting blood-borne antigens for contact with immune-responsive cells. |
| | (2) | The role of the lymph nodes in collecting blood-borne antigens for contact with immune-responsive cells. |
| B |
25. |
(1) |
The time required to observe a reaction resulting from a Type I hypersensitivity. |
| | (2) | The time required to observe a reaction resulting from a Type IV hypersensitivity. |
39. (2 points) Give the equation that describes the affinity constant for an antibody-antigen interaction.
40. (2 points) Draw the “Triangle of Relationships” that I described in class.
41. (4 points) Draw the general structure of an IgG immunoglobulin showing i) the Fc region, ii) the antigen binding region, iii) the constant regions and iv) the variable regions.
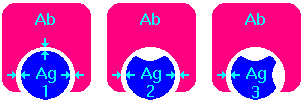
42. (4 points) Describe the concept of antigen cross-reactivity. Use a picture to illustrate the concept.
43. (6 points) A researcher studying several new bacterial exotoxins performed the following experiment. A number of mice were divided into 2 groups. The first set of mice were given six different doses of Toxin A and the second group of mice were given six different doses of Toxin B. After 24 hours, the percentage of dead mice was determined and the results are shown in the table.
Use these data to 1) draw a graph, 2) determine the LD50 for the two treatments and 3) indicate which of the two treatments had the greatest virulence.
44. (6 points) In the following experiment, three groups of guinea pigs (GP) were employed. On day 1, group 1 guinea pigs received an intravenous injection of bovine serum albumin (BSA) designed to induce IgE. Also on day 1, group 2 guinea pigs received a non-lethal dose of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Group 3 guinea pigs were given a cookie. After two weeks (day 14), the animals were tested for their responsiveness to BSA and a lethal dose of M. tuberculosis. Complete the following table by indicating whether the guinea pigs in each test group lived (+) or died (-).